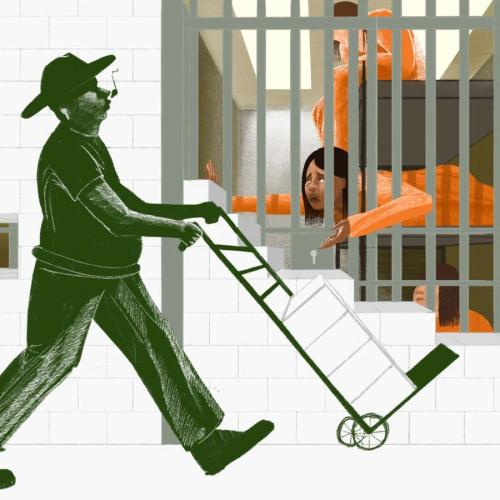
Prison-Industrial Complex
Revealing News on the Prison-Industrial Complex
"The United States has less than 5 percent of the world's population. But it has almost a quarter of the world's prisoners. Americans are locked up for crimes — from writing bad checks to using drugs — that would rarely produce prison sentences in other countries. And in particular they are kept incarcerated far longer than prisoners in other nations."
~~ New York Times article on the corrupt prison-industrial complex in the US, 4/23/08
Dear friends,

Like the military-industrial complex, the prison-industrial complex is rife with a great variety of corruption and cover-ups, as has been widely reported in the press. With greed and graft rampant, the prisons industry often breeds criminals and sends innocent people to their death. It's time for us to wake up and do something about it.
Below is a collection of revealing excerpts from major media news articles showing the dire need for major transformation in our prisons system. It's time to get the greed and profit out of punishment and replace it with true rehabilitation, as is happening now in some Scandinavian countries. It's time to turn the prison-industrial complex into a place where the huge amount of money spent is used not only to keep us safe, but to give public offenders a real chance to turn their lives around.
You can make a difference right now by educating yourself to the disturbing truths mentioned in the articles below, and then spreading this important news not only to your friends and colleagues, but to politicians and others who can help to transform the prison-industrial complex from a money machine into a place designed for justice and rehabilitation. See the "What you can do" section below for more on how you can play your role in this important endeavor. And thanks for caring.
With very best wishes for a transformed world,
Fred Burks for PEERS and WantToKnow.info
Former White House interpreter and whistleblower
Note: Explore our full index to revealing excerpts of key major media news articles on dozens of engaging topics. And read excerpts from 20 of the most revealing news articles ever published.
Prisons, Privatization, Patronage
2012-06-22, New York Times
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/06/22/opinion/krugman-prisons-privatization-patro...
The New York Times has published several terrifying reports about New Jersey’s system of halfway houses — privately run adjuncts to the regular system of prisons. The horrors described are part of a broader pattern in which essential functions of government are being both privatized and degraded. So what’s really behind the drive to privatize prisons? One answer is that privatization can serve as a stealth form of government borrowing, in which governments avoid recording upfront expenses (or even raise money by selling existing facilities) while raising their long-run costs in ways taxpayers can’t see. Another answer is that privatization is a way of getting rid of public employees. But the main answer, surely, is to follow the money. As more and more government functions get privatized, states become pay-to-play paradises, in which both political contributions and contracts for friends and relatives become a quid pro quo for getting government business. Are the corporations capturing the politicians, or the politicians capturing the corporations? One thing the companies that make up the prison-industrial complex — companies like Community Education or the private-prison giant Corrections Corporation of America — are definitely not doing is competing in a free market. They are, instead, living off government contracts. And ... despite many promises that prison privatization will lead to big cost savings, such savings — as a comprehensive study by the Bureau of Justice Assistance, part of the U.S. Department of Justice, concluded — “have simply not materialized.” A corrupt nexus of privatization and patronage [is] undermining government across much of our nation.
Note: Have you noticed that crime rates are at the lowest in many years, yet prison spending continues to skyrocket? Is something wrong with this picture?
U.S. prison population dwarfs that of other nations
2008-04-23, New York Times
http://www.nytimes.com/2008/04/23/world/americas/23iht-23prison.12253738.html
The United States has less than 5 percent of the world's population. But it has almost a quarter of the world's prisoners. Indeed, the United States leads the world in producing prisoners, a reflection of a relatively recent and now entirely distinctive American approach to crime and punishment. Americans are locked up for crimes — from writing bad checks to using drugs — that would rarely produce prison sentences in other countries. And in particular they are kept incarcerated far longer than prisoners in other nations. Criminologists and legal scholars in other industrialized nations say they are mystified and appalled by the number and length of American prison sentences. The United States has, for instance, 2.3 million criminals behind bars, more than any other nation. The United States ... has 751 people in prison or jail for every 100,000 in population. (If you count only adults, one in 100 Americans is locked up.) The median among all nations is about 125, roughly a sixth of the American rate. "Far from serving as a model for the world, contemporary America is viewed with horror," James Whitman, a specialist in comparative law at Yale, wrote last year in Social Research. Prison sentences here have become "vastly harsher than in any other country to which the United States would ordinarily be compared," Michael Tonry, a leading authority on crime policy, wrote. Indeed, said Vivien Stern, a research fellow at the prison studies center in London, the American incarceration rate has made the United States "a rogue state, a country that has made a decision not to follow what is a normal Western approach."
Note: Many people are not aware that violent crime in the US has dropped by over 50% in the last 15 years. Yet the prison population continues to grow rapidly at the same time. For more on this, click here.
FBI Investigates Prison Company
2014-03-07, ABC News/Associated Press
http://abcnews.go.com/US/wireStory/apnewsbreak-fbi-investigates-prison-compan...
The FBI has launched an investigation of the Corrections Corporation of America over the company's running of an Idaho prison with a reputation so violent that inmates dubbed it "Gladiator School." CCA has operated Idaho's largest prison for more than a decade, but last year, CCA officials acknowledged it had understaffed the Idaho Correctional Center by thousands of hours in violation of the state contract. CCA also said employees falsified reports to cover up the vacancies. The announcement came after an Associated Press investigation showed CCA sometimes listed guards as working 48 hours straight to meet minimum staffing requirements. The understaffing has been the subject of federal lawsuits and a contempt of court action against CCA. The ACLU sued on behalf of inmates at the Idaho Correctional Center in 2010, saying the facility was so violent that inmates called it "Gladiator School" and that understaffing contributed to the high levels of violence there. In 2012, a Boise law firm sued on behalf of inmates contending that CCA had ceded control to prison gangs so that they could understaff the prison and save money on employee wages, and that the understaffing led to an attack by one prison gang on another group of inmates that left some of them badly injured.
Note: If the above link fails, use this one for the same Associated Press article on corruption in the prison-industrial complex reported on the website of the UK's Guardian.
Inside the Shadowy Business of Prison Phone Calls
2015-07-02, International Business Times
http://atavist.ibtimes.com/fcc-prison-telecom-industry
The prison phone business is a wildly complex, fiercely secretive and enormously lucrative industry. Over the last decade, [this] business has become a scandalous industry, characterized by lawsuits, exorbitant fees, high phone rates and monopolistic relationships between public jails and private companies that openly offer kickbacks to local sheriffs. "This is about shifting the cost of the police state onto the backs of the poor people being policed," says Paul Wright, executive director of Human Rights Defense Center. [There are] an estimated 2.2 million inmates currently behind bars in America. If you've ever tried to call an inmate, there's a good chance you've heard of Securus, or its main competitor, Global Tel*Link (GTL). The two companies reportedly make up about 80 percent of the prison phone business, which drives about $1.2 billion per year in revenues. In the last few years, Securus, especially, has emerged into one of the largest, if not most secretive, prison technology companies in the business. The company employs 1,000 associates in 46 states, contracts with 2,600 jails and prisons across North America, and provides service to more than 1 million inmates and their families. Securus earned $114.6 million in profits 2014, on revenues of about $404 million. When companies like Securus send proposals to jails and prisons around the country, they offer a percentage of the call rate back to the sheriff's office. It's typical for commissions to range anywhere from 40 percent and 80 percent.
Note: Read more on the rampant corruption around phones in the prison-industrial complex in this Huffington Post article.
Prison Spending Outpaces All but Medicaid
2009-03-03, New York Times
http://www.nytimes.com/2009/03/03/us/03prison.html?partner=rss&emc=rss&pagewa...
One in every 31 adults, or 7.3 million Americans, is in prison, on parole or probation, at a cost to the states of $47 billion in 2008, according to a new study. Criminal correction spending is outpacing budget growth in education, transportation and public assistance, based on state and federal data. Only Medicaid spending grew faster than state corrections spending, which quadrupled in the past two decades, according to [a new report] by the Pew Center on the States, the first breakdown of spending in confinement and supervision in the past seven years. The increases in the number of people in some form of correctional control occurred as crime rates declined by about 25 percent in the past two decades. As states face huge budget shortfalls, prisons, which hold 1.5 million adults, are driving the spending increases. Pew researchers say that as states trim services like education and health care, prison budgets are growing. Those priorities are misguided, the study says. “States are looking to make cuts that will have long-term harmful effects,” said Sue Urahn, managing director of the Pew Center on the States. “Corrections is one area they can cut and still have good or better outcomes than what they are doing now.” About $9 out of $10 spent on corrections goes to prison financing (that includes money spent to house 780,000 people in local jails). One in 11 African-Americans, or 9.2 percent, are under correctional control, compared with one in 27 Latinos (3.7 percent) and one in 45 whites (2.2 percent).
Note: Crime is down 25%, yet prison spending is 400% of what it was 20 years ago. Is there anything strange here? The prison-industrial complex is mighty big and in many ways mighty corrupt.
The Innocent on Death Row
2014-09-04, New York Times
http://www.nytimes.com/2014/09/04/opinion/the-innocent-on-death-row.html
In late September 1983, an 11-year-old girl named Sabrina Buie was found murdered in a soybean field in Robeson County. She had been raped, beaten with sticks and suffocated with her own underwear. Within days, police got confessions from two local teenagers, Henry Lee McCollum, 19 at the time, and his half brother, Leon Brown, who was 15. Both were convicted and sentenced to death. On [September 2], a state judge ordered both men freed after multiple pieces of evidence, some of which had never been turned over to defense lawyers, proved that neither Mr. McCollum nor Mr. Brown was responsible for the crime. DNA taken from a cigarette found at the crime scene matched a different man, Roscoe Artis, who is already serving life in prison for a similar murder committed just weeks after Sabrina Buie’s killing. Virtually everything about the arrests, confessions, trial and convictions of Mr. McCollum and Mr. Brown was polluted by official error and misconduct. No physical evidence linked either man to the crime, so their false confessions, given under duress, were the heart of the case the prosecutors mounted against them. Both men’s confessions were handwritten by police after hours of intense questioning without a lawyer or parent present. Neither was recorded, and both men have maintained their innocence ever since. Equally disturbing, Mr. Artis was a suspect from the start. Three days before the murder trial began, police requested that a fingerprint from the crime scene be tested for a match with Mr. Artis, who had a long history of sexual assaults against women. The test was never done, and prosecutors never revealed the request to the defense.
Hundreds of U.S. inmates sentenced to death are innocent, researchers say
2014-04-29, Chicago Tribune/Reuters
http://articles.chicagotribune.com/2014-04-29/news/sns-rt-us-usa-crime-death-...
As many as 300 people who were sentenced to death in the United States over a three-decade period were likely innocent. Dozens of defendants sentenced to death in recent years have been exonerated before their sentences could be carried out, but many more were probably falsely convicted, said University of Michigan professor Samuel Gross, the study's lead author. "Our research adds the disturbing news that most innocent defendants who have been sentenced to death have not been exonerated," Gross wrote in the study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. In their research, Gross and his colleagues examined the 7,482 U.S. death sentence convictions between 1973 and 2004. Of those, 117 had been exonerated in recent years, thanks to the efforts of numerous groups and a tide of public attention to issues surrounding the death penalty. Gross and his co-authors ... estimated that about 4 percent of those sentenced to death were actually innocent, nearly three times the number exonerated during that period. Once inmates' sentences are commuted to life, they are far less likely to be exonerated, mostly because there are fewer legal resources given to their cases, Gross said. "If you were never sentenced to death, you never had the benefit - if you call it a benefit - of that process," he said. Although the study focuses on a period ending 10 years ago, the percentage of false death sentence convictions likely holds true today, Gross said.
FBI admits flaws in hair analysis over decades
2015-04-18, Washington Post
http://www.washingtonpost.com/local/crime/fbi-overstated-forensic-hair-matche...
The Justice Department and FBI have formally acknowledged that nearly every examiner in an elite FBI forensic unit gave flawed testimony in almost all trials in which they offered evidence against criminal defendants over more than a two-decade period before 2000. Of 28 examiners with the FBI Laboratory’s microscopic hair comparison unit, 26 overstated forensic matches in ways that favored prosecutors in more than 95 percent of the 268 trials reviewed so far, according to the National Association of Criminal Defense Lawyers (NACDL) and the Innocence Project, which are assisting the government with the country’s largest post-conviction review of questioned forensic evidence. The cases include those of 32 defendants sentenced to death. Of those, 14 have been executed or died in prison, the groups said under an agreement with the government to release results after the review of the first 200 convictions. The admissions mark a watershed in one of the country’s largest forensic scandals, highlighting the failure of the nation’s courts for decades to keep bogus scientific information from juries, legal analysts said. The question now, they said, is how state authorities and the courts will respond to findings that confirm long-suspected problems with subjective, pattern-based forensic techniques — like hair and bite-mark comparisons — that have contributed to wrongful convictions in more than one-quarter of 329 DNA-exoneration cases since 1989.
Note: For more along these lines, see concise summaries of deeply revealing news articles on the threats to civil liberties posed by government corruption from reliable major media sources.
10 Questions With Bryan Stevenson
2014-10-27, Time Magazine
http://time.com/3512675/bryan-stevenson-interview/
TIME: Your book Just Mercy is about getting legal help for poor people in Alabama. What are the biggest impediments? BRYAN STEVENSON (Lawyer and founder of the Equal Justice Initiative): We have a criminal-justice system that treats you better if you’re rich and guilty than if you’re poor and innocent. I don’t believe that America’s system is shaped by culpability. I think it’s shaped by wealth. TIME: 1 in 3 black men in the U.S. under 30 is in jail, on probation or on parole. Is this the scariest stat? STEVENSON: That 1 in 3 black males born in 2001 is expected to go to jail or prison during their lifetimes is more astonishing because it’s about the future. And 1 in 6 Latino boys. That wasn’t true in the 20th century. TIME: What do you say to people who say, “It’s easy to not go to jail–don’t commit a crime”? STEVENSON: In this country we have a presumption of guilt that follows young kids of color. I’ve represented 10-year-olds being prosecuted as adults. They are put in an adult jail. It’s so unnecessary–we have juvenile facilities. No one defends it, and yet we still have 10,000 children in an adult jail or prison. TIME: What’s the role of the corporations that build prisons? STEVENSON: Corporations have really corrupted American criminal justice by creating these perverse incentives where they actually pay legislators to create new crimes so that we can maintain these record-high-level rates of imprisonment. These companies spend millions of dollars a year on lobbying. Prison spending has gone from $6 billion in 1980 to $80 billion today.
Note: For details about Stevenson's uphill battle as a legal advocate for the poor, read the complete transcript of the Time interview summarized above dealing with the prison-industrial complex.
Plantations, Prisons and Profits
2012-05-26, New York Times
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/05/26/opinion/blow-plantations-prisons-and-profit...
“Louisiana is the world’s prison capital. The state imprisons more of its people, per head, than any of its U.S. counterparts. First among Americans means first in the world. Louisiana’s incarceration rate is nearly triple Iran’s, seven times China’s and 10 times Germany’s.” That paragraph opens a devastating eight-part series published this month by The Times-Picayune of New Orleans about how the state’s largely private prison system profits from high incarceration rates and tough sentencing, and how many with the power to curtail the system actually have a financial incentive to perpetuate it. The picture that emerges is one of convicts as chattel and a legal system essentially based on human commodification. • One in 86 Louisiana adults is in the prison system, which is nearly double the national average. • More than 50 percent of Louisiana’s inmates are in local prisons, which is more than any other state. The national average is 5 percent. • Louisiana leads the nation in the percentage of its prisoners serving life without parole. • Nearly two-thirds of Louisiana’s prisoners are nonviolent offenders. The national average is less than half. In the early 1990s, the state was under a federal court order to reduce overcrowding, but instead of releasing prisoners or loosening sentencing guidelines, the state incentivized the building of private prisons. But, in what the newspaper called “a uniquely Louisiana twist,” most of the prison entrepreneurs were actually rural sheriffs. They saw a way to make a profit and did.
Note: To read the powerful 8-part investigation of Louisiana's prison-industrial complex from the New Orleans Times-Picayune, click here.
How America's death penalty murders innocents
2012-05-21, The Guardian (One of the UK's leading newspapers)
http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/cifamerica/2012/may/21/america-death-...
The US criminal justice system is a broken machine that wrongfully convicts innocent people, sentencing thousands of people to prison or to death for the crimes of others, as a new study reveals. The University of Michigan law school and Northwestern University have compiled a new National Registry of Exonerations – a database of over 2,000 prisoners exonerated between 1989 and the present day, when DNA evidence has been widely used to clear the names of innocent people convicted of rape and murder. Of these, 885 have profiles developed for the registry's website, exonerationregistry.org. The details are shocking. Death row inmates were exonerated nine times more frequently than others convicted of murder. One-fourth of those exonerated of murder had received a death sentence, while half of those who had been wrongfully convicted of rape or murder faced death or a life behind bars. Ten of the inmates went to their grave before their names were cleared. The leading causes of wrongful convictions include perjury, flawed eyewitness identification and prosecutorial misconduct. "The most important thing we know about false convictions is that they happen and on a regular basis … Most false convictions never see the light of the day," said University of Michigan law professors Samuel Gross and Michael Shaffer, who wrote the study. "Nobody had an inkling of the serious problem of false confessions until we had this data," said Rob Warden, executive director of the Center on Wrongful Convictions at Northwestern University.
Why is Sweden closing its prisons?
2013-12-01, The Guardian (One of the UK's leading newspapers)
http://www.theguardian.com/society/2013/dec/01/why-sweden-closing-prisons
Swedish prisons have long had a reputation around the world as being liberal and progressive. The head of Sweden's prison and probation service, Nils Oberg, announced in November that four Swedish prisons are to be closed due to an "out of the ordinary" decline in prisoner numbers. Although there has been no fall in crime rates, between 2011 and 2012 there was a 6% drop in Sweden's prisoner population, now a little over 4,500. A similar decrease is expected this year and the next. The Swedes [have] managed to maintain a broadly humane approach to sentencing, even of the most serious offenders: jail terms rarely exceed 10 years; those who receive life imprisonment can still apply to the courts after a decade to have the sentence commuted to a fixed term, usually in the region of 18 to 25 years. Sweden was the first country in Europe to introduce the electronic tagging of convicted criminals and continues to strive to minimise short-term prison sentences wherever possible by using community-based measures – proven to be more effective at reducing reoffending. The overall reoffending rate in Sweden stands at between 30 and 40% over three years – around half that in the UK. One likely factor that has kept reoffending down and the rate of incarceration in Sweden below 70 per 100,000 head of population – less than half the figure for England and Wales – is that the age of criminal responsibility is set at 15. Unlike the UK, where a life sentence can be handed down to a 10-year-old, in Sweden no young person under the age of 21 can be sentenced to life and every effort is made to ensure that as few juvenile offenders as possible end up in prison.
Note: For a Time magazine article showing how Norway's prisons actually rehabilitate prisoners so that they can more easily fit back in society, click here. For a treasure trove of great news articles which will inspire you to make a difference, click here.
America's private prison system is a national disgrace
2013-06-13, The Guardian (One of the UK's leading newspapers)
http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/2013/jun/13/aclu-lawsuit-east-mississ...
Privatization [of government functions] often comes with a lack of oversight and a series of abuses. One particularly stunning example is the American prison system, the realities of which should be a national disgrace. Some of those realities are highlighted in a recent lawsuit filed by the American Civil Liberties Union on behalf of prisoners at the East Mississippi Correctional Facility (EMCF). EMCF houses severely mentally ill prisoners, with the supposed intent of providing both incarceration and treatment. Instead, the ACLU contends, the facility, which is operated by private contractors, is rife with horrific abuses. The complaint lists a litany of such horrors, [including]: Rampant rapes. Placing prisoners in solitary confinement for weeks, months or even years at a time. Rat infestations so bad that vermin crawl over prisoners. Many suicide attempts, some successful. Denying or delaying treatment for infections and even cancer. Stabbings, beatings and other acts of violence. Malnourishment and chronic hunger. Officers who deal with prisoners by using physical violence. The [US] prison system is increasingly built and run by for-profit corporations, who have a financial interest in increasing the number of people in prison while decreasing the amount of money it costs to house them. Since 1980, the US prison population has grown by 790%. We have the largest prison population of any nation in the history of the world.
Can Forgiveness Play a Role in Criminal Justice?
2013-01-06, New York Times
http://www.nytimes.com/2013/01/06/magazine/can-forgiveness-play-a-role-in-cri...
Most modern justice systems focus on a crime, a lawbreaker and a punishment. But a concept called “restorative justice” considers harm done and strives for agreement from all concerned — the victims, the offender and the community — on making amends. And it allows victims, who often feel shut out of the prosecutorial process, a way to be heard and participate. In this country, restorative justice takes a number of forms, but perhaps the most prominent is restorative-justice diversion. There are not many of these programs — a few exist on the margins of the justice system in communities like Baltimore, Minneapolis and Oakland, Calif. — but, according to a University of Pennsylvania study in 2007, they have been effective at reducing recidivism. Typically, a facilitator meets separately with the accused and the victim, and if both are willing to meet face to face without animosity and the offender is deemed willing and able to complete restitution, then the case shifts out of the adversarial legal system and into a parallel restorative-justice process. All parties — the offender, victim, facilitator and law enforcement — come together in a forum sometimes called a restorative-community conference. Each person speaks, one at a time and without interruption, about the crime and its effects, and the participants come to a consensus about how to repair the harm done. The methods are mostly applied in less serious crimes, like property offenses in which the wrong can be clearly righted. The processes are designed to be flexible enough to handle violent crime like assault, but they are rarely used in those situations.
Note: This deeply moving and highly educational piece from the New York Times Magazine about the power of restorative justice is well worth reading in its entirety at the link above.
Breaking the hold of corporate welfare on America's incarceration industry
2012-12-19, The Guardian (One of the UK's leading newspapers)
http://www.guardian.co.uk/commentisfree/2012/dec/19/corporate-welfare-incarce...
The US Department of Justice released a report this week showing that 26 states have recorded decreases in their prison populations during 2011. California boasted the biggest decline of over 15,000 prisoners and several other states including New York and Michigan reported drops of around 1,000 prisoners each. This is the third consecutive year that the population has declined, and as a result, at least six states have closed or are attempting to close approximately 20 prisons. But sadly, because incarceration has become a virtual jobs program in many states and because certain corporations are profiting handsomely from the incarceration binge that has been in place for the past few decades, the reduction in prison populations and prison closures is being met with huge resistance. According to a recent report by the Sentencing Project called On the Chopping Block (pdf), which detailed all the prison closures and attempted closures in the past year, several state governors have been dragged into legal battles with state employees and unions who want the prisons to stay open. The private prisons, which are funded by the taxpayer ... need to generate revenue to keep their shareholders happy. For them, the bottom line is keeping their prisons full, regardless of need or cost. Last year, the Corrections Corporation of America (CCA) came under fire when it emerged that they sent a letter to 48 states offering to take over any prisons going spare – with the small caveat that they be guaranteed 90% occupancy for the next 20 years.
Guantánamo leaks lift lid on world's most controversial prison
2011-04-25, The Guardian (One of the UK's leading newspapers)
http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2011/apr/25/guantanamo-files-lift-lid-prison
More than 700 leaked secret files on the Guantánamo detainees lay bare the inner workings of America's controversial prison camp in Cuba. The US military dossiers ... reveal how ... many prisoners were flown to the Guantánamo cages and held captive for years on the flimsiest grounds, or on the basis of lurid confessions extracted by maltreatment. The 759 Guantánamo files, classified "secret", cover almost every inmate since the camp was opened in 2002. More than two years after President Obama ordered the closure of the prison, 172 are still held there. The files depict a system often focused less on containing dangerous terrorists or enemy fighters, than on extracting intelligence. Among inmates who proved harmless were an 89-year-old Afghan villager, suffering from senile dementia, and a 14-year-old boy who had been an innocent kidnap victim. The documents also reveal: • US authorities listed the main Pakistani intelligence service, the Inter-Services Intelligence Directorate (ISI), as a terrorist organisation. • Almost 100 of the inmates who passed through Guantánamo are listed by their captors as having had depressive or psychotic illnesses. Many went on hunger strike or attempted suicide. • A number of British nationals and residents were held for years even though US authorities knew they were not Taliban or al-Qaida members.
Note: For many key reports on government secrecy from major media sources, click here.
Sentenced to Serving the Good Life in Norway
2010-07-12, Time Magazine
http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,2000920,00.html
On Bastoy, an island 46 miles south of Oslo, [125] residents live in brightly colored wooden chalets, spread over one square mile of forest and gently sloping hills. They go horseback riding and throw barbecues, and have access to a movie theater, tanning bed and, during winter, two ski jumps. Despite all its trappings, Bastoy island isn't an exclusive resort: it's a prison. Bastoy's governor ... describes it as the world's first human-ecological prison — a place where inmates learn to take responsibility for their actions by caring for the environment. Prisoners grow their own organic vegetables, turn their garbage into compost and tend to chickens, cows, horses and sheep. The prison generally emphasizes trust and self-regulation: Bastoy has no fences, the windows have no bars, and only five guards remain on the island after 3 p.m. In an age when countries from Britain to the U.S. cope with exploding prison populations by building ever larger — and, many would say, ever harsher — prisons, Bastoy seems like an unorthodox, even bizarre, departure. But Norwegians see the island as the embodiment of their country's long-standing penal philosophy: that traditional, repressive prisons do not work, and that treating prisoners humanely boosts their chances of reintegrating into society. Norway's system produces overwhelmingly positive results. Within two years of their release, 20% of Norway's prisoners end up back in jail. In the U.K. and the U.S., the figure hovers between 50% and 60%. Of course, Norway's ... prison roll lists a mere 3,300 inmates, a rate of 70 per 100,000 people, compared with 2.3 million in the U.S., or 753 per 100,000 — the highest rate in the world.
Note: Why aren't other countries taking heed of Norway's excellent example? Part of the reason is that some companies make massive profits from the prison-industrial complex. For more on this, click here.
Why we spend billions to keep half a million unconvicted people behind bars
2015-06-11, Washington Post
http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/wonkblog/wp/2015/06/11/why-we-spend-billi...
At any given time, roughly 480,000 people sit in America's local jails awaiting their day in court, according to an estimate by the International Centre for Prison Studies. These are people who have been charged with a crime, but not convicted. They remain innocent in the eyes of the law. Three quarters of them ... are nonviolent offenders, arrested for traffic violations, or property crimes, or simple drug possession. Many will be found innocent and have their charges dropped completely. Defendants who [are] detained before trial [wait] a median of 68 days in jail. Many ... are forced to wait simply because they can't afford to post bail. A 2013 analysis by the Drug Policy Alliance ... found that nearly 40 percent of New Jersey's jail population fell into this category. People sit behind bars not because they're dangerous, or because they're a flight risk, but simply because they can't come up with the cash. A recent analysis by the Vera Institute ... found that 41 percent of New York City's inmates were sitting in jail on a misdemeanor charge because they couldn't meet a bail of $2,500 or less. For low income people, the consequences of a pre-trial detention, even a brief one, can be disastrous. And in many cases, these people will eventually be found to be innocent. Some civil rights reformers [argue] that bail policies are tantamount to locking people up for being poor. We spend somewhere in the ballpark of $17 billion dollars annually to keep innocent people locked up as they await trial.
Note: For more, read this New York Times article. For more along these lines, see concise summaries of deeply revealing news articles about income inequality and systemic corruption in the prison-industrial-complex.
Ohio Men Wrongly Convicted of Murder After 39 Years Released
2014-11-21, NBC News
http://www.nbcnews.com/news/crime-courts/ohio-men-wrongly-convicted-murder-af...
Two Ohio men wrongly accused of murder experienced freedom for the first time in nearly four decades on Friday morning, but said they don’t harbor bitterness over their unjust imprisonment. A Cleveland judge on Wednesday had dropped all charges against Ricky Jackson, 57, and Wiley Bridgeman, 60, allowing for the pair’s release. Jackson was 19 when he was convicted along with Bridgeman and Bridgeman’s brother, Ronnie, in the 1975 shooting death and robbery of Harold Franks, a Cleveland-area money order salesman. Testimony from a 12-year-old witness helped point to Jackson as the triggerman and led a jury to convict. The witness, Edward Vernon, now 53, recanted his testimony last year, saying he was coerced by detectives, according to Cuyahoga County court documents. Vernon wrote in a 2013 affidavit that he never saw the murder take place, but he was told by detectives that if he didn’t testify against Jackson, his parents would be arrested. The Ohio Innocence Project, which took up the case, said Jackson had been the longest-held U.S. prisoner to be exonerated. Jackson was originally sentenced to death, but that sentence was vacated because of a paperwork error. The Bridgeman brothers remained on death row until Ohio declared the death penalty unconstitutional in 1978. “One of them came within 20 days of execution before Ohio ruled the death penalty unconstitutional” said Mark Godsey, director of the Ohio Innocence Project.
Note: Watch an inspiring five-minute video of this beautiful man who was originally sentenced to death based largely on the testimony of a 12 year old, who it turns out was coerced by police to blame him. And how many have been wrongly executed that we will never know about? For more along these lines, see concise summaries of deeply revealing civil liberties articles from reliable major media sources.
Note: Explore our full index to revealing excerpts of key major media news articles on dozens of engaging topics. And read excerpts from 20 of the most revealing news articles ever published.
Finding Balance: WantToKnow.info Inspiration Center
WantToKnow.info believes it is important to balance disturbing cover-up information with inspirational writings which call us to be all that we can be and to work together for positive change. For an abundance of uplifting material, please visit our Inspiration Center.
- Contact your media and political representatives to inform them of this vital information on the prison-industrial complex. Urge them to study and bring publicity to this important topic. Invite them to read this article and explore the links included.
- Read lots more reliable, verifiable information on major cover-ups and corruption, all serving as a call to work together for positive change.
- Explore inspiring ideas on how we can work together to create a new paradigm.
- For a heart and mind expanding online course, see the free Insight Course.
- Spread this news on the prison-industrial complex to your friends and colleagues, and bookmark this article on key social networking websites using the "Share" icon on this page, so that we can fill the role at which the major media is sadly failing. Together, we can make a difference.
See our exceptional archive of revealing news articles.
Please support this important work: Donate here
www.momentoflove.org - Every person in the world has a heart
www.personalgrowthcourses.net - Dynamic online courses powerfully expand your horizons
www.WantToKnow.info - Reliable, verifiable information on major cover-ups
www.weboflove.org - Strengthening the Web of Love that interconnects us all
Subscribe here to the WantToKnow.info email list (two messages a week)