Inspiring: Healing Our Earth Media Articles
Below are key excerpts of inspiring news articles on healing our Earth from reliable news media sources. If any link fails to function, a paywall blocks full access, or the article is no longer available, try these digital tools.
For further exploration, delve into our Inspiration Center.
Fifty years ago, Congress voted to override President Richard Nixon’s veto of the Clean Water Act. It has proved to be one of the most transformative environmental laws ever enacted. At the time of the law’s passage, hundreds of millions of gallons of raw sewage was dumped by New York City into the Hudson River every day. This filth was compounded by industrial contaminants emptied into the river along much of its length. The catch basin for all of this was New York Harbor, which resembled an open sewer. At its worst, 10 feet of raw human waste blanketed portions of the harbor bottom. Health advisories against eating fish from the Hudson remain, but its ecology has largely recovered, thanks to the law, which imposed strict regulations on what could be discharged into the water by sewage treatment plants, factories and other sources of pollution. Today people swim in organized events in New York Harbor, which would have been unthinkable in 1972 when the law was passed. Across the country, billions of dollars were also spent to construct and improve sewage treatment plants, leading to recoveries of other urban waterways. Cleaner water has made the harbor far more hospitable, and other steps have helped to rebuild life there, like fishing restrictions and the removal of some dams on tributaries in the Hudson River watershed. The bald eagle has made a strong comeback, taking advantage of the harbor’s resurgent fish life. In December 2020 a humpback whale was seen in the Hudson just one mile from Times Square.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Certain mushroom species have the ability to consume polyurethane, one of the main ingredients in plastic products. Some scientists believe that these natural composters could be the key to cleaning up our planet. Mycoremediation is the natural process that fungi use to degrade or isolate contaminants in the environment. A 2020 study published in Biotechnology Reports found that mycoremediation applied to agricultural wastes like pesticides, herbicides, and cyanotoxins is more cost-effective, eco-friendly, and effective. A project using the mycelium (the vegetative part of the mushroom similar to a plant’s root system) of two common mushrooms made headlines in 2014. Using Pleurotus ostreatus, also known as the oyster mushroom, and Schizophyllum commune, aka the split gill mushroom, the team was able to turn plastic into human-grade food. The mushrooms were cultivated on circular pods made of seaweed-derived gelatin filled with UV-treated plastics. As the fungus digests the plastic, it grows around the edible base pods to create a mycelium-rich snack after just a few months. According to a study by the University of Rajasthan in India, plastic-eating mushrooms can sometimes absorb too much of the pollutant in their mycelium, and therefore cannot be consumed. If more research is performed regarding the safety aspects, however, mycoremediation through mushroom cultivation could perhaps address two of the world’s greatest problems: waste and food scarcity.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Near the southern border of the Pine Ridge Reservation in South Dakota, a curved translucent roof peeks out a few feet above the dusty plains. Below ground, at the bottom of a short flight of stairs, the inside of this 80ft-long sleek structure is bursting with life – pallets of vivid microgreens, potato plants growing from hay bales and planters full of thick heads of Swiss chard and pak choi. This is an underground greenhouse, or walipini, and the harvesters are members of the Oglala Sioux Tribe. It is one of at least eight underground greenhouses that, over the past decade, have been built or are being constructed on the reservation – which has one of the highest poverty rates in the US. Some hope they can help solve the interconnected problems of the lack of affordable, nutritious food and the difficulties of farming in the climate crisis. Today, more than half of the residents of Oglala Lakota county, one of three counties within the boundaries of the reservation, live below the poverty line. Food access is a huge problem. The 2.1m-acre reservation is classified as a “food desert” with only a handful of grocery stores. And health outcomes, including diet related diseases, are poor – about 50% of adults over 40 have diabetes. Neil Mattson, professor and greenhouse extension specialist at Cornell University’s School of Integrative Plant Science, says underground greenhouses could help to usher in more year-round food production across the northern US but they are still fairly new in the country.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Underwater noise due to human activities at sea can harm marine biodiversity, leading for example to hearing impairment and behavioural disturbances. EU experts have adopted recommendations on maximum acceptable levels for impulsive (for example from oil and gas exploration and extraction) and continuous (such as from shipping) underwater noise. The new limits mean, that to be in tolerable status, no more than 20% of a given marine area, can be exposed to continuous underwater noise over a year Similarly, no more than 20% of a marine habitat can be exposed to impulsive noise over a given day, and no more than 10% over a year. These underwater noise pollution limits deliver on the Zero Pollution Action Plan and are the first of this kind at global level. The threshold values will contribute to set limits on where and for how long marine habitats can be exposed to underwater noise. Impulsive underwater noise, such as from oil and gas exploration, occurs in about 8 % of the EU’s seas: it is particularly present in large areas of the Baltic, North and Celtic Seas, and the Mediterranean area. Maritime traffic is the main source of continuous underwater noise. With 27% of its area subject to shipping, the Mediterranean Sea sees the highest shipping traffic in the EU. This is followed by the Baltic Sea (19 % of the area). Overall, only 9% of the EU’s sea area has no shipping traffic. EU Member States will now need to take these threshold values into account when they update their marine strategies.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Beginning in the late 1990s, as landfills in the crowded capital area approached their limits, South Korea implemented a slate of policies to ease what was becoming seen as a trash crisis. The government banned burying organic waste in landfills in 2005, followed by another ban against dumping leachate – the putrid liquid squeezed from solid food waste – into the ocean in 2013. Universal curbside composting was implemented that same year, requiring everyone to separate their food from general waste. In 1996, South Korea recycled just 2.6% of its food waste. Today, South Korea recycles close to 100% annually. Ease-of-use and accessibility have been crucial to the success of the South Korean model. “South Korea’s waste system, especially in terms of frequency of collection, is incredibly convenient compared to other countries,” says Hong Su-yeol, a waste expert and director of Resource Recycling Consulting. “Some of my peers working at non-profits overseas say that disposal should be a little bit inconvenient if you want to discourage waste but I disagree: I think that it should be made as easy as possible as long as it goes hand-in-hand with other policies that attack the problem of reducing waste itself.” National and municipal governments in South Korea have been actively investing in urban farming programs, which include composting courses. These sort of community-based efforts might be where the US can shine, increasing initial access to composting options in cities that presently have few other options.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Joost Bakker believes a house can be more than a place to live: it can be a self-sustaining weapon against the climate crisis. A new Australian documentary explores his bold blueprint. Bakker – a multi-disciplinary designer, no-waste advocate and the film’s eponymous protagonist – has long been something of a provocateur. In 2020, the Dutch-born, Australian-raised designer’s two decades of high-concept sustainability projects came to a head when he hit go on the construction of Future Food System. Erected in one of the busiest areas of Melbourne, the off-grid, three-storey house and urban farm produced all of its own power and food. Even the cooking gas was generated from human and food waste. “We can have it all,” Bakker [says]. “We can have houses covered with biology, plants, ecosystems and waterfalls. It’s not necessary for us to be destroying the planet or killing each other with materials that are making us sick. The infrastructure is already there. It’s just about reimagining our suburbs and reimagining our buildings.” Shadowing Bakker throughout the project from set-up to pack-down, was film-maker Nick Batzias ... who squeezes plenty of action into the pacy 90-minute documentary. The bulk of the film focuses on the building’s green-thinking initiatives. Steam from the showers is used to grow mushrooms; the foundation-less building is anchored by self-watering garden beds filled with 35 tonnes of soil.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
A new rooftop wind harvesting device is capable of generating 50 percent more electricity than solar panels for the same cost, according to its inventors, a Texas-based startup called Aeromine Technologies. The new technology replaced the blades found in traditional wind turbines with an aerodynamic system that harvests energy from the airflow that’s created above a building, which makes it silent and safe for birds and other wildlife. These units produce the same amount of power as up to 16 solar panels. As their company website states: "Aeromine’s patented aerodynamic design captures and amplifies building airflow in wind speeds as low as 5 m.p.h., similar to the airfoils on a race car. Unlike turbines that require rotating rotor blades and many moving parts, making them prone to maintenance issues, the motionless and durable Aeromine solution generates more energy in less space." This is a game-changer ... helping corporations meet their resilience and sustainability goals with an untapped distributed renewable energy source. The Aeromine system can utilize a small footprint on a building’s roof, leaving ample space for existing solar and utility infrastructure. It provides commercial property owners, who are facing increased energy costs and rising demand for features such as electric vehicle charging stations, with an effective new tool. Aeromine’s patented technology was validated through joint research with Sandia National Laboratories and Texas Tech University.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
When floods devastated Bangkok more than a decade ago, Thai landscape architect Kotchakorn Voraakhom became determined to help her sinking hometown fight this deadly climate threat. The floods "changed my life," said Voraakhom. "I started using the tools of landscape architecture (to tackle) climate change." The 2011 floods killed hundreds and displaced millions. "For us, climate change is primarily a water crisis," she said. "Our people can feel its impacts in their daily lives, each year through worsening floods, rising sea levels, and severe drought." In many sinking cities, including Bangkok, the current urban infrastructure is not fit for purpose and is "reducing our ability to adapt," said Voraakhom, noting that many of Bangkok's waterways and canals have been destroyed or have fallen into disrepair. "For us, as a city of water, the only way is to go back to our amphibious culture and reclaim the relationship with water." The architect said she integrates nature and water into her designs to create landscapes that help alleviate flooding and add greenery to densely populated cities. Voraakhom also created Asia's largest rooftop farm, Siam Green Sky, transforming 22,400 square meters (241,000 square feet) into a lush haven. The farm, which recycles food waste from restaurants in the building below and uses it as plant fertilizer, also slows down, soaks up and stores large amounts of rainwater. It is then used to grow vegetables, herbs and fruit, as well as rice.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Swarms of honeybees can generate as much electrical charge as a thunderstorm, new research shows. In a study published in the journal iScience on Monday, researchers from the University of Bristol ... discovered this phenomenon by chance. Biologist Ellard Hunting [said] that the Bristol team was studying how different organisms use the static electric fields that are everywhere in the environment. Atmospheric electricity has a variety of functions, mainly in shaping weather events and helping organisms, for example in finding food. “Flowers have an electric field and bees can sense these fields. And these electric fields of flowers can change when it has been visited by a bee, and other bees can use that information to see whether a flower has been visited,” Hunting explained. Having set up equipment to measure atmospheric electric fields at the university’s field station, which features several honeybee hives, Hunting and his team noticed that whenever the bees swarmed, there was “a profound effect on atmospheric electric fields,” even though the weather hadn’t changed. All insects create a charge during flight as a result of friction in the air, with the size of the charge varying between species. Individual bees carry a charge that is small enough to be overlooked by researchers, so “this effect (in swarming bees) came as a surprise,” Hunting said. They found that, depending on the swarm density, the atmospheric charge could be similar to that of a storm cloud, thunderstorm or electrified dust storm.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Natural disasters like earthquakes and hurricanes can level entire towns, and for the search and rescue teams trying to find survivors, it’s a painstaking task. But an unlikely savior is being trained up to help out: rats. The project, conceived of by Belgian non-profit APOPO, is kitting out rodents with tiny, high-tech backpacks to help first responders search for survivors among rubble in disaster zones. “Rats are typically quite curious and like to explore – and that is key for search and rescue,” says Donna Kean, a behavioral research scientist and leader of the project. In addition to their adventurous spirit, their small size and excellent sense of smell make rats perfect for locating things in tight spaces, says Kean. The rats are currently being trained to find survivors in a simulated disaster zone. They must first locate the target person in an empty room, pull a switch on their vest that triggers a beeper, and then return to base, where they are rewarded with a treat. While the rodents are still in the early stages of training, APOPO is collaborating with the Eindhoven University of Technology to develop a backpack, which is equipped with a video camera, two-way microphone, and location transmitter to help first responders communicate with survivors. APOPO has been training dogs and rats at its base in Tanzania in the scent detection of landmines and tuberculosis for over a decade. Its programs use African Giant Pouched Rats, which have a longer lifespan in captivity of around eight years.
Note: Don't miss the images of these adorable and heroic rats at the link above. Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
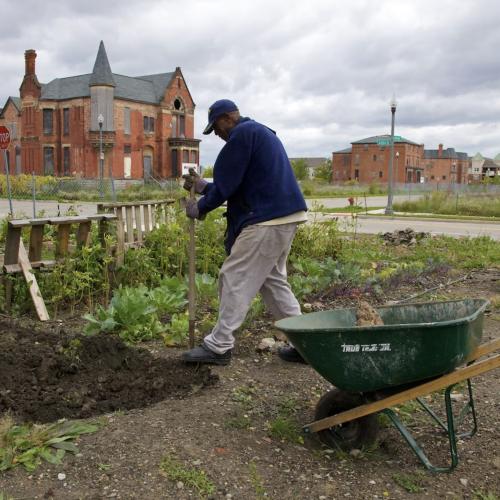
[Pamela] McGhee and her neighbors are participating in a pilot program to build zero-waste systems for Detroit. It’s something they say the city sorely needs. For decades, Detroit was home to one of the country’s largest waste incinerators. East Side residents formed Breathe Free Detroit, one of several groups behind a successful campaign to shut down the incinerator; the plant closed in 2019. Now, that same group is working with the city to develop a composting system. Many ... see a direct line between composting and recycling and improving their community health. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, food waste is the most common material found in landfills and sent to incinerators in the U.S., comprising 24% of landfill materials and 22% of combusted municipal solid waste. But Detroit organizers didn’t have much experience with communitywide composting, so when they began developing a program, they turned to an unlikely mentor more than 8,000 miles away: the Mother Earth Foundation in the Philippines. Over the past 20 years, the organization has earned a reputation for training low-income communities, government agencies, civic organizations, and businesses in zero-waste practices. The two groups organized monthly calls, in which Mother Earth Foundation organizers offered advice based on their experiences setting up community composting systems. Members of Mother Earth Foundation and community organizers in Detroit plan to visit each other’s cities early next year.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
"Don't get dirty!" was once a constant family refrain, as parents despairingly watched their children spoil their best clothes. Today, many parents may secretly wish their children had the chance to pick up a bit of grime. According to recent research, the dirt outside is teaming with friendly microorganisms that can train the immune system and build resilience to a range of illnesses, including allergies, asthma and even depression and anxiety. Certain natural materials, such as soil and mud ... contain surprisingly powerful microorganisms whose positive impact on children's health we are only beginning to fully understand. Our brains evolved in natural landscapes, and our perceptual systems are particularly well suited to wild outdoor spaces. Supporting this theory, one study from 2009 found that children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) were better able to concentrate following a 20-minute walk in the park, compared to a 20-minute walk on the streets of a well-kept urban area. People who grow up on farms are generally less likely to develop asthma, allergies, or auto-immune disorders like Crohn's disease [due to] their childhood exposure to a more diverse range of organisms in the rural environment. Michele Antonelli, a doctor from Italy ... has researched the ways that mud therapies can influence health. People with [skin] disorders ... seem to have an impoverished community of organisms. "These microorganisms can play a major role in many major chronic diseases," he says.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Australia will set aside at least 30% of its land mass for conservation in a bid to protect plants and animals in the island continent famed for species found nowhere else in the world, Environment Minister Tanya Plibersek said. Australia has lost more mammal species than any other continent and has one of the worst rates of species decline among the world's richest countries, a five-yearly environmental report card released in July by the government showed. That report showed the number of species added to the list of threatened species or in a higher category of risk grew on average by 8% from the previous report in 2016. "The need for action to protect our plants, animals and ecosystems from extinction has never been greater," Plibersek said in a statement. By prioritising 110 species and 20 places, Plibersek said the areas managed for conservation will be increased by 50 million hectares. Australia ... is home to unique animals like koalas and platypus although their numbers have been dwindling due to extreme weather events and human encroachment into their habitats. Koalas along much of the east coast were listed as endangered in February. Australia has been battered recently by frequent extreme weather events including the devastating bushfires in 2019 and 2020 in the east that killed ... billions of animals and burned an area nearly half the size of Germany.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Enzymes that rapidly break down plastic bags have been discovered in the saliva of wax worms, which are moth larvae that infest beehives. The enzymes are the first reported to break down polyethylene within hours at room temperature. The discovery came after one scientist, an amateur beekeeper, cleaned out an infested hive and found the larvae started eating holes in a plastic refuse bag. The researchers said the study showed insect saliva may be “a depository of degrading enzymes which could revolutionise [the cleanup of polluting waste]”. Polyethylene makes up 30% of all plastic production and is used in bags and other packaging that make up a significant part of worldwide plastic pollution. The only recycling at scale today uses mechanical processes and creates lower-value products. Chemical breakdown could create valuable chemicals or, with some further processing, new plastic, thereby avoiding the need for new virgin plastic made from oil. The enzymes can be easily synthesised and overcome a bottleneck in plastic degradation, the researchers said, which is the initial breaking of the polymer chains. That usually requires a lot of heating, but the enzymes work at normal temperatures, in water and at neutral pH. Previous discoveries of useful enzymes have been in microbes, with a 2021 study indicating that bacteria in oceans and soils across the globe are evolving to eat plastic. It found 30,000 different enzymes that might degrade 10 different types of plastic.
Note: This research was published in the journal Nature Communications. Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Recent research suggests that plants are far from the stationary automatons that most of us think of them as. And though they don't have brains in the same way most animals do, plants seem to possess a different set of evolutionary tools that suggest they may experience consciousness, albeit in a radically different way from us. Dr. Paco Calvo has an upcoming book, co-authored with Natalie Lawrence, called "Planta Sapiens: Unmasking Plant Intelligence." Calvo works at the MINT Lab (Minimal Intelligence Lab) at the University of Murcia in Spain. "Sentience, we may say, makes sense for life, as an essential underpinning to the business of living," Calvo explained. "And it is very unlikely that plants are not far more aware than we intuitively assume." To the "skeptics" who insist that consciousness must be tied to a central nervous system, and that plants would not need to evolve consciousness in the first place, "even if 'consciousness', as understood in vertebrates, is generated by complex neuronal systems, there is no objective way of knowing that subjective experience has not evolved with entirely different kinds of hardware in other organisms," Calvo argued. "We have no evidence to conclude that no brain means no awareness. It is certainly true that we cannot yet know if plants are conscious. But we also cannot assume that they are not." Calvo added, "Plants ... might well have significant conscious experience, although there is no way for us to intuit it nor for them to communicate it to us."
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
Ants can be more effective than pesticides at helping farmers produce food, according to new research. They are better at killing pests, reducing plant damage and increasing crop yields, according to the first systematic review of ants’ contributions to crop production. Ants are generalist predators and hunt pests that damage fruits, seeds and leaves, leading to a drop in crop yields. A greater diversity of ants generally provides more protection against a wider range of pests, the study found. The analysis looked at 17 crops, including citrus, mango, apple and soya bean in countries including the US, Australia, the UK and Brazil. “In general, with proper management, ants can be useful pest controls and increase crop yield over time. Some ant species have similar or higher efficacy than pesticides, at lower costs,” researchers wrote in the paper published in Proceedings of Royal Society B. There are more ants than any other insect, making up half of the planet’s insect biomass. There are at least 14,000 known species of ant, with many more likely to remain unknown. Citrus growers in China have used ants in farming for centuries, and the insects have also been used to help control forest pests in Canada, cocoa pests in Ghana and crop pests in Nigeria. Dr Patrick Milligan, from the University of Nevada Pringle Lab ... said the findings were “both heartening and not at all surprising”. He added: “They offer a neat and tidy description of ant-derived benefits that are ubiquitous across ecological and agricultural systems.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
The amount of coral in some areas of the Great Barrier Reef is at its highest in 36 years, according to a new report from the Australian Institute of Marine Science. From August 2021 to May 2022, the central and northern regions of the Great Barrier Reef had hard coral cover levels of 33% and 36%, respectively. Coral cover decreased by 4% in the southern region, due to an outbreak of crown-of-thorns starfish. The Australian agency found that 87 coral reefs generally had low levels of acute stress from things such as cyclones and increases in the crown-of-thorns starfish population. The area surveyed represents two-thirds of the Great Barrier Reef. Almost half of the reefs studied had between 10% and 30% hard coral cover, while about a third of the reefs had hard coral cover levels between 30% and 50%, the report said. While higher water temperatures led to a coral bleaching event in some areas in March, the temperatures did not climb high enough to kill the coral, the agency said. Coral in the Great Barrier Reef is resilient, and has been able to recover from past disturbances, the Institute said. But the stressors impacting it have not gone away for long. The agency's outlook shows more frequent and long-lasting heatwaves, cyclones and crown-of-thorns starfish. "Therefore, while the observed recovery offers good news for the overall state of the [Great Barrier Reef], there is increasing concern for its ability to maintain this state," the report said.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
We are learning just how smart insects can be. As I show in my new book, “The Mind of a Bee,” the latest research indicates that even tiny-brained bees are profoundly intelligent creatures that can memorize not only flowers but also human faces, solve problems by thinking rather than by trial and error, and learn to use tools by observing skilled bees. They even appear to experience basic emotions, or at least something like optimism and pessimism. Bees have a “dance language” by which they can inform others in the hive of the precise location of a rewarding flower patch. The symbolic language involves repeating the motor patterns (“dances”) of a knowledgeable bee on the vertical honeycomb. The movements make reference to gravity and the direction of the sun; since it’s dark in the hive, bees that want to learn from the dancer need to touch its abdomen with their antennae. Sometimes, such dances are displayed at night, when no foraging takes place: The dancer appears to think about locations visited on the previous day, without an obvious need to do so at the time. The observation that bees are most likely sentient beings has important ethical implications. Many species of bees are threatened by pesticides and wide-scale habitat loss, and that this spells trouble because we need these insects to pollinate our crops. But is the utility of bees the only reason they should be protected? I don’t think so. Bees have a rich inner world and unique perception, and, like humans, are able to think, enjoy and suffer.
Note: Watch an amazing, highly educational PBS documentary on the life of bees. Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
For the first time in 30 years, legislation has been put forward to address catastrophic wildlife loss in the EU. Legally binding targets for all member states to restore wildlife on land, rivers and the sea were announced today, alongside a crackdown on chemical pesticides. In a boost for UN negotiations on halting and reversing biodiversity loss, targets released by the European Commission include reversing the decline of pollinator populations and restoring 20% of land and sea by 2030, with all ecosystems to be under restoration by 2050. The commission also proposed a target to cut the use of chemical pesticides in half by 2030 and eradicate their use near schools, hospitals and playgrounds. Frans Timmermans, executive vice-president of the commission, said the laws were a step forward in tackling the “looming ecocide” threatening the planet. Around €100bn (£85bn) will be available for spending on biodiversity, including the restoration of ecosystems. The target of 2030 to cut the use of pesticides will give farmers time to find alternatives. The proposals, which campaigners have hailed as a potential milestone for nature, could become law in around a year. Member states would have to create restoration plans to show the commission how they would reach the targets set, and if they fail to follow through they would face legal action. Priority ecosystems include those with the greatest power to remove and store carbon, as well as buffer the impacts of natural disasters.
Note: Explore a treasure trove of concise summaries of incredibly inspiring news articles which will inspire you to make a difference.
The artist, writer and technologist James Bridle begins "Ways of Being" with an uncanny discovery: a line of stakes tagged with unfathomable letters and numbers in thick marker pen. The region of [Greece] is rich in oil, we learn, and the company that won the contract to extract it from the foothills of the Pindus mountains is using "cognitive technologies" to "augment ... strategic decision making." The grid of wooden stakes left by "unmarked vans, helicopters and work crews in hi-vis jackets" are the "tooth- and claw-marks of Artificial Intelligence, at the exact point where it meets the earth." "Ways of Being" sets off on a tour of the natural world, arguing that intelligence is something that "arises ... from thinking and working together," and that "everything is intelligent." We hear of elephants, chimpanzees and dolphins who resist and subvert experiments testing their sense of self. We find redwoods communicating through underground networks. In the most extraordinary result of all, in 2014 the Australian biologist Monica Gagliano showed that mimosa plants can remember a sudden fall for a month. Ever since the Industrial Revolution, science and technology have been used to analyze, conquer and control. But "Ways of Being" argues that they can equally be used to explore and augment connection and empathy. The author cites researchers studying migration patterns with military radar and astronomers turning telescopes designed for surveillance on Earth into instruments for investigating the dark energy of the cosmos.
Note: Read a thought-provoking article featuring a video interview with artist and technologist James Bridle as he explores how technology can be used to reflect the innovative and life-enhancing capacities of non-human natural systems. For more along these lines, see concise summaries of deeply revealing news articles on mysterious nature of reality from reliable major media sources.
Important Note: Explore our full index to key excerpts of revealing major media news articles on several dozen engaging topics. And don't miss amazing excerpts from 20 of the most revealing news articles ever published.